Identification of maternal cell contamination
Identification of maternal cell contamination
Short tandem repeat (STR) genotyping detection combined with multiplex fluorescent PCR technology is used to identify maternal cell contamination in samples for prenatal diagnosis of genetic diseases and investigation of causes of miscarriage. It has strong specificity and sensitivity, and the results are accurate It is reliable and can better solve the problem of individual identification in mixed samples.
Maternal cell contamination identification, detection of 10% maternal cell contamination
Maternal Cell Contamination (MCC) of prenatal diagnosis and abortion tissue samples identification
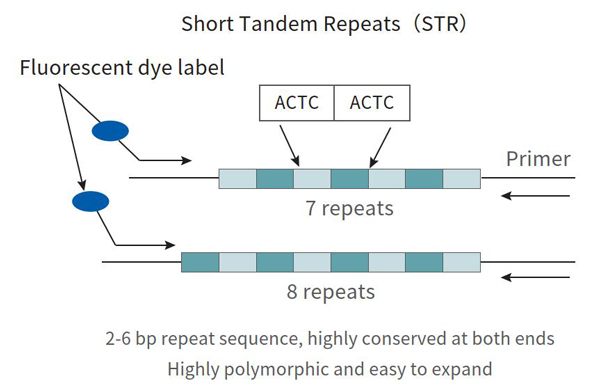
Amplify 21 STR genetic loci in a single tube to improve detection accuracy
Highly polymorphic, distantly located on chromosomes, no linkage affect
Hundreds of thousands of sample tested, great repeatability
Single tube amplification, complete PCR within 1.5h, and a complete STR profile can be obtained as low as 1ng of DNA
PCR instrument + Genetic analyzer
PCR instrument: Life Technologies Holdings Pte Ltd: Veriti, Veriti Dx, 9700
Genetic analyzer: Life Technologies Holdings Pte Ltd: 3500 Dx, 3500 xL Dx; Seqstudio.
Multiplex fluorescent PCR-capillary electrophoresis

[1] Allen S, Mountford R , Butler A , et al. Practice Guidelines for the Testing for Maternal Cell Contamination (MCC) in Prenatal Samples for Molecular Studies. Guidelines ratified by the UK Clinical Molecular Genetics Society (2008).
[2] Sarah, T., et al. "ACMG Standards and Guidelines for constitutional cytogenomic microarray analysis, including postnatal and prenatal applications: revision 2013. " Genetics in medicine : official journal of the American College of Medical Genetics (2013).
[3] Expert consensus on the application of low-depth whole-genome sequencing technology in prenatal diagnosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Medical Genetics, 2019, 36(4):293-296.
[4] Consensus on data analysis, interpretation and reporting standardization of prenatal genetic diagnosis of copy number variation and homozygous regions [J]. Chinese Journal of Medical Genetics, 2020, 37(07):701-708.
※ This product is only for scientific research use, and this information is only for reference by relevant medical professionals. Please refer to the instruction manual for details of contraindications or precautions.
[ENG]Maternal_blood_contamination.pdf:Reference:[ENG]Maternal_blood_contamination.pdf